Pairing Ion Exchange and Reverse Osmosis for Optimal Water Recycling
As sustainable water management initiatives have grown in popularity, it’s important to understand the tools available to treat wastewater and process streams for reuse. While ion exchange (IX) and reverse osmosis (RO) are two very different separation technologies, both can be valuable components in water treatment systems—especially for facilities looking to recycle or reuse their wastewater. Here, we’ll look at the benefits that ion exchange and reverse osmosis offer, and how they can be combined to serve complementary roles in water treatment.

Understanding the role of ion exchange and reverse osmosis in wastewater treatment
Wastewater treatment is a complex process that is performed in multiple stages. At minimum, a wastewater treatment train will usually include preliminary, primary, and secondary treatment steps, which focus on removal of large particles, solids, and organic matter. Depending upon the wastewater stream and applicable discharge requirements, this may be sufficient for some facilities’ needs, but for facilities wanting to reuse their wastewater, treatment will usually proceed to a tertiary stage.
Tertiary wastewater treatment is typically where ion exchange (IX) and/or reverse osmosis (RO) would be used, as these technologies are effective for removal of dissolved materials and/or specific pollutants that persist following secondary treatment. Tertiary treatment allows facilities to achieve a higher level of water quality, producing a stream that is suitable for reuse, or clean enough to discharge to waterways or receiving POTWS with very stringent wastewater discharge standards. In recent years, both IX and RO have seen increased adoption in wastewater treatment and water recycling systems due to their efficiency in removing stubborn contaminants.
Whether motivated by water scarcity, an evolving regulatory landscape, or environmental stewardship initiatives, industrial facilities are increasingly embracing investment in water reuse and recycling initiatives. Already, many facilities are using IX and/or RO to treat wastewater for reuse in boilers and cooling towers. Other common uses of IX and RO include treating process streams for reuse in food/beverage processing, textile production, pulp/paper manufacturing, and semiconductor manufacturing. There are also growing instances of pharmaceutical manufacturers employing onsite wastewater treatment systems with IX and /or RO technologies to ensure safe discharge of their waste streams, since most POTW facilities are not equipped to handle their complex wastewater. In this way, IX and RO can be helpful tools for keeping problematic chemicals from entering waterways. These strategies help to reduce wastewater, while also conserving valuable resources.
What contaminants do ion exchange and reverse osmosis remove?
Both IX and RO can remove many of the same contaminants, including:
- Total dissolved solids (TDS)
- Metals and minerals
- Sulfates and detergents
- Nitrates and nitrites
- PFAS (PFOS, PFOA)
- Pesticides and other chemicals
In addition to the above list, RO can also remove the following contaminants:
- Pathogens (e.g. bacteria, viruses)
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
In contrast, IX is not an effective treatment strategy for either VOCs or pathogens.
How does ion exchange work?
Ion exchange (IX) is a water treatment technology selectively removes contaminants based on their chemical structure. During a treatment cycle, the stream is passed through a specialized medium known as an IX resin, which attracts and holds certain charged particles, thereby separating them out of the liquid stream. Since IX is a selective treatment technology, facilities can target certain contaminants for removal without wasting resources on removing other constituents that may be innocuous or even desirable if left in the stream.
Pros and cons of ion exchange
Ion exchange is an excellent solution for targeted contaminant removal, offering a variety of benefits with some minor drawbacks compared to other water treatment technologies:
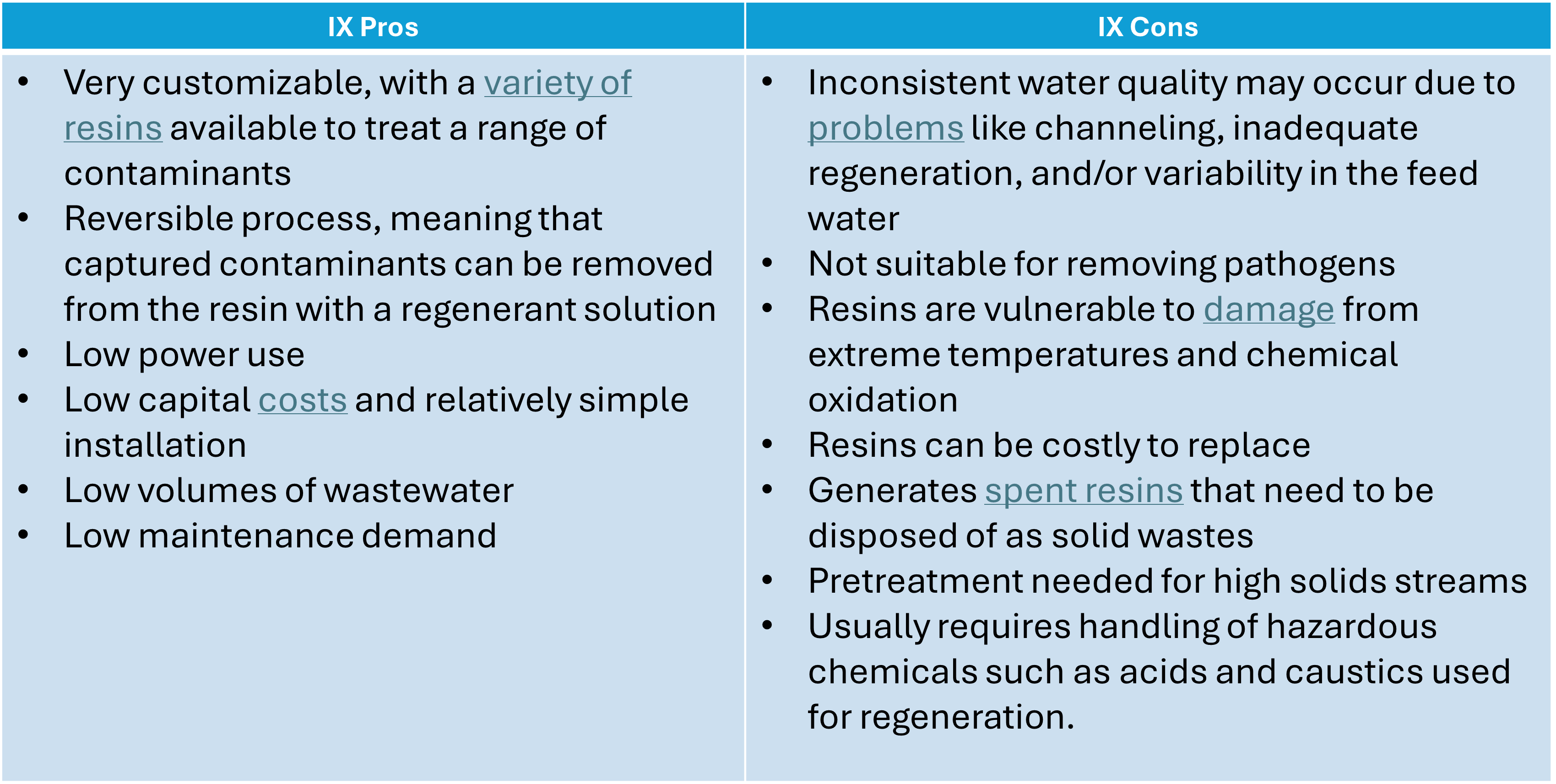
IX is at its best when used for removal of a narrow set of identified contaminants. A properly designed system will leverage IX in ways that minimize its potential drawbacks are quite minimal, allowing facilities to efficiently and affordably remove problematic constituents to make a stream suitable for reuse, further treatment, or even discharge.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a physical separation technology that offers broad-spectrum contaminant removal. RO units work by applying pressure to a liquid stream to force it through a specialized semi-permeable membrane. Any contaminants too large to fit through the microscopic pores in the membrane are retained as part of a concentrated waste (or “retentate”) stream, while purified water permeates through the membrane. In this way, RO removes a complex mix of contaminants at once, allowing facilities to produce a high-purity filtrate with removal rates as high at 99% or more.
Pros and cons of reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is an excellent choice for removing a variety of contaminants in fewer steps, yielding a range of benefits along with some drawbacks:
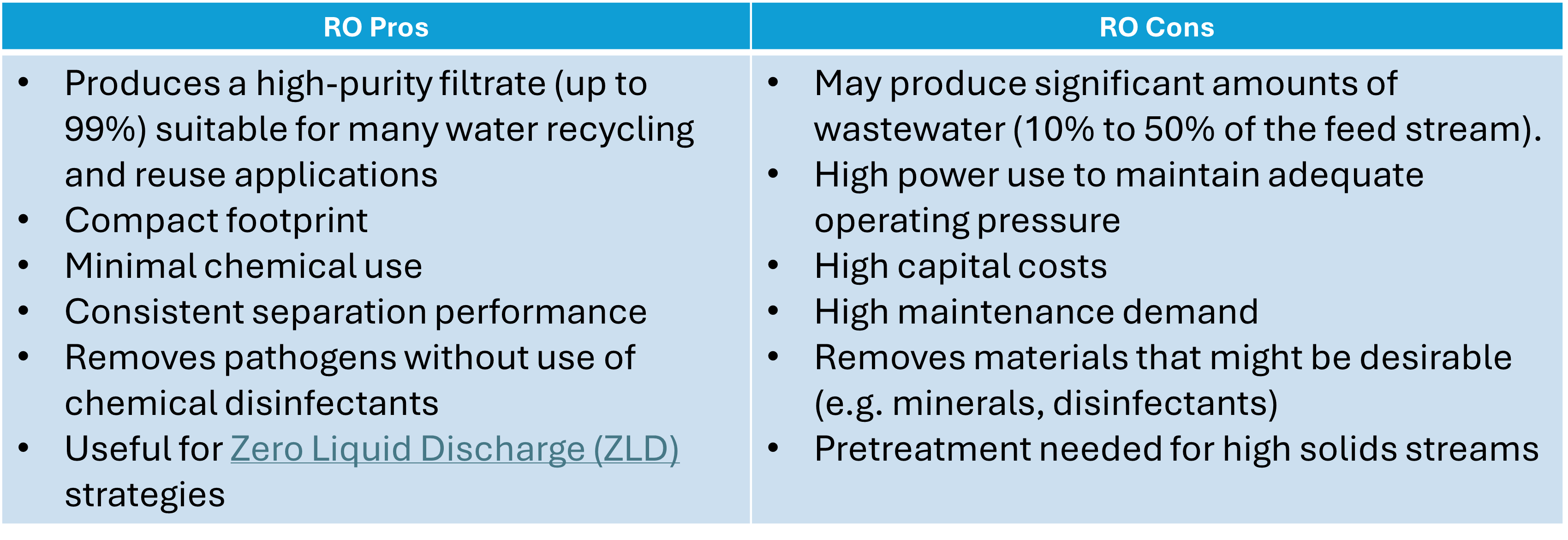
Compared to other water treatment technologies, RO delivers reliable removal of a wide range of contaminants, making it an effective solution for achieving high levels of water purity required by water reuse applications, or compliance with stringent discharge standards. For best performance, RO should be used on streams with a low to moderate concentration of contaminants.
Using IX and RO together
IX and RO are valuable tools for a wide array of wastewater treatment and process separation applications, each of which offering their own unique benefits and limitations. These differences make IX and RO excellent complements to one another, and there are many applications where the two are used together to achieve a desired result. For example, IX is often used to reduce hardness ahead of RO in a treatment train. By removing hardness-causing metals like calcium and magnesium, IX helps to prevent scale buildup on RO membranes, which can prolong membrane service life and potentially allow the RO unit to go longer between cleaning and maintenance cycles. Additionally, by reducing the contaminant load, IX can also help downstream RO units perform more efficiently and achieve lower reject rates, which can help facilities conserve more of their water for reuse, and minimize the amount of wastewater generated by the RO system.
IX may alternatively be deployed as a final polishing step after RO. This arrangement leverages IX technology to remove trace ionic or organic contaminants remaining after RO separation, yielding water with an extremely low contaminant load (<10 parts per billion), otherwise known as ultrapure water (UPW). A IX polisher can be an efficient means of producing UPW demanded by various industrial processes, including power generation, as well as water used in the manufacture of chemicals, microelectronics, and pharmaceuticals, among other applications.
Regardless of whether IX and RO are used independently or together, it is important to note that both are susceptible to clogs from larger particles, which can lead to poor performance, excess maintenance, and shortened service life of consumables like IX resins and RO membranes. As such, streams that are high in suspended solids should be pretreated ahead of either IX or RO, or, if used in a wastewater treatment train, IX and/or RO should be used after secondary treatment.
How SAMCO can help?
SAMCO has over 40 years’ experience designing and building custom process separation and wastewater treatment systems for a range of industries and applications. Our experts have a deep knowledge of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, and a range of other separation technologies, so please feel free to contact us with your questions. Our engineers are here to assist you in exploring available technologies and understanding the steps involved in developing a proper solution for your goals.
Or, if you’ve already got a specific project in mind and want some help in planning your budget, reach out to request a quote. We can walk you through the steps for developing the proper solution and realistic cost for your needs.
